Design One Bit Full Adder Using Multiplexers
You are here: Home / Electronics / What is Multiplexer and Types of Multiplexing Techniques
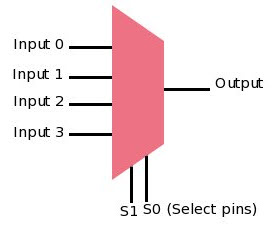
Multiplexer
A Multiplexer is a device that allows one of several analog or digital input signals which are to be selected and transmits the input that is selected into a single medium. Multiplexer is also known as Data Selector. A multiplexer of 2n inputs has n select lines that will be used to select input line to send to the output. Multiplexer is abbreviated as Mux.
MUX sends digital or analog signals at higher speed on a single line in one shared device. It recovers the separate signals at the receiving end. The Multiplexer boosts or amplifies the information that later transferred over network within a particular bandwidth and time.This article gives an overview of what is multiplexer and types of multiplexer.
What is Multiplexer
The Multiplexer acts as a multiple-input and single-output switch. Multiple signals share one device or transmission conductor such as a copper wire or fiber optic cable.In telecommunications, the analog or digital signals transmitted on several communication channels by a multiplex method. These signals are single-output higher-speed signals. A 4-to-1 multiplexer contains four input signals and 2-to-1 multiplexer has two input signals and one output signal.
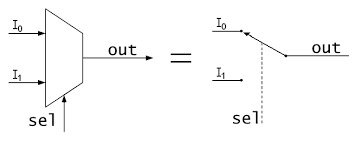
Schematic Symbol for Multiplexer
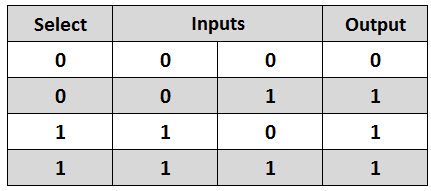
Truth Table for 2 to 1 Multiplexer
Multiplexers are also extended with same name conventions as DE multiplexers. A 4 to 1 multiplexer circuit is as below
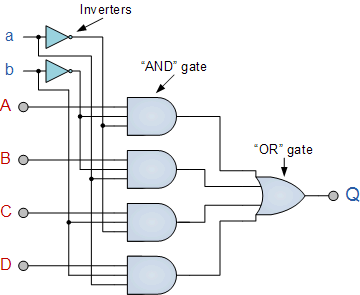
4 to 1 Multiplexer Circuit
Types of Multiplexing
The technique of transmitting multiple signals over a single medium is defined as Multiplexing. It is a technique showed at physical layer of OSI model.
The different types of multiplexing technologies are as below
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
- Conventional Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
- Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer (ROADM)
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- Add/Drop Multiplexing (ADM)
- Inverse Multiplexing (IMUX)
Types of Multiplexer
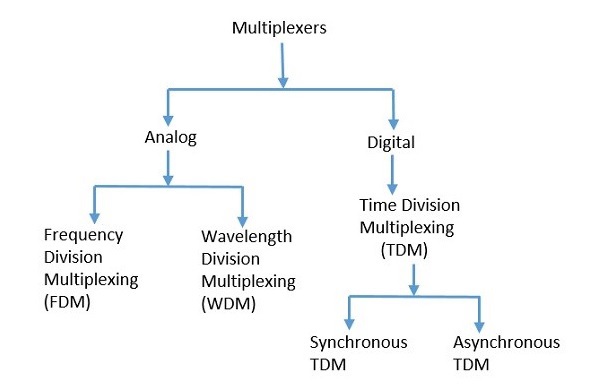
Types of Multiplexer
Frequency Division Multiplexing
Frequency Division Multiplexing is a technique which uses various frequencies to combine many streams of data for sending signals over a medium for communication purpose. It carries frequency to each data stream and later combines various modulated frequencies to transmission.Television Transmitters are the best example for FDM, which uses FDM to broad cast many channels at a time.
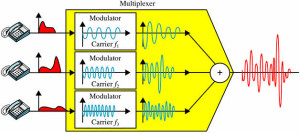
Frequency Division Multiplexing
In this type of multiplexing, signals are generated by sending different device-modulated carrier frequencies, and these modulated signals are then combined into a single signal that can be transported by the link. To accommodate the modulated signal, the carrier frequencies are separated with enough bandwidth, and these bandwidth ranges are the channels through which different signals travel. These channels can be separated by unused bandwidth. Some of the examples for the time division multiplexing include radio and television signal transmission.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is analog multiplexing technique and it modulates many data streams on light spectrum. This multiplexing is used in optical fiber. It is FDM optical equivalent.Various signals in WDM are optical signal that will be light and were transmitted through optical fiber.WDM similar to FDM as it mixes many signals of different frequencies into single signal and transfer on one link.Wavelength of wave is reciprocal to its frequency, if wavelength increase then frequency decreases.Several light waves from many sources are united to get light signal which will be transmitted across channel to receiver.
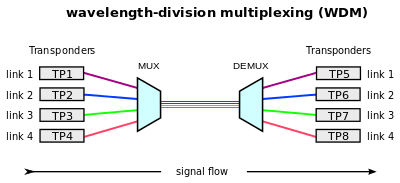
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
The main principle in using prisms is that they bend a light beam depending on angle of incidence and frequency of light wave or ray. At receiver end the light signal is split into different light waves by demux. This type of merging and breaking of light wave made by a prism. Single prism is used at the end of sender for multiplexing and other prism is used at receiver end for demultiplexing as shown in fig.
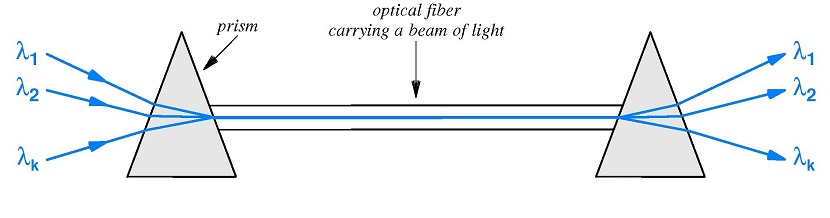
Usage of PRISM in WDM
WDM used in Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). It utilizes various optical fiber lines that are multiplexed and demultiplexed.
Time Division Multiplexer
TDM is one of types of multiplexers which join data streams by allotting every stream different time slot in a set. It frequently transfers or sends various time slots in an order over one transmission channel. TDM attaches PCM data streams.
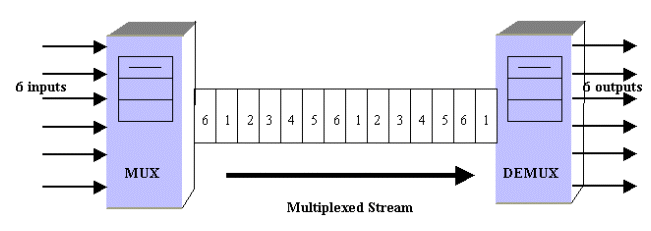
Time Division Multiplexer
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer
In Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, an optical technology used to expand bandwidth onto fiber optic. Bit rate and protocol are independent and these are the main advantage of DWDM. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) operated by combining different signals simultaneously at different wavelengths. On fiber is changed to multiple fibers. By increasing the carrier capacity of fiber from 2.5Gb/s to 20 Gb/s, an eight OC 48 signals can be multiplexed into single fiber.Single fibers are able to transfer data at a speed upto 400 GB/s due to DWDM.DWDM transfers data or information in IP, SONET, ATM and Ethernet It also carries different type of traffic at a range of speeds on an optical channel.
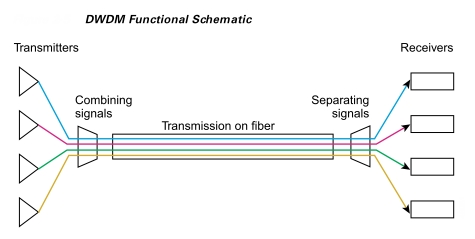
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer
Statistical Multiplexer
It allows to share a single line of data for multiplexer RS-232 devices. Error correction will be performed in order to ensure the transmission an error-free one. The word "Statistical" refers to its capability to receive advantage of statics of many RS-232 devices means terminal and PC users.Each PC averages less than 5% of its potential data rate.
This type of multiplexer permits the sum of terminal and PC rates in which it extends composite link speed between multiplexers. This is due the reason that the keyboards are idle. These types of multiplexers requires buffer.
Difference between Mux and Demux
- A Multiplexer is a device used to communicate by means of a medium with combination of multiple signals.
- A DE multiplexer is a process of separating multiplexed signals from transmission line.
- These both Mux and DMux are mixed into single device which has the capability to process outgoing and incoming signals
- An electronic multiplexer is a multiple-input, single-output switch.
- A DE multiplexer as a single-input, multiple-output switch
- MUX allows many signals to share one device.
- Example: one A/D converter or one communication line
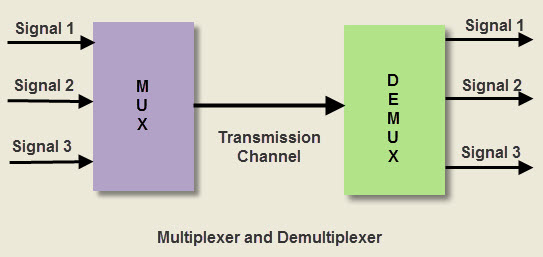
Difference between MUX and Demux
List of ICs Which Provide Multiplexing
The 7400 series has several ICs that contain multiplexers
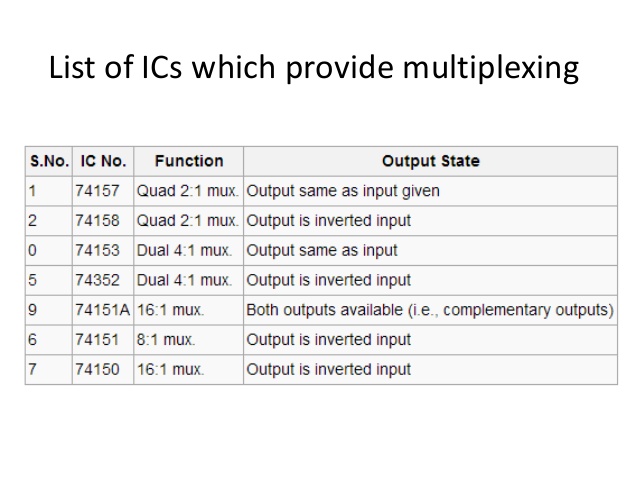
List of ICs which Provide Multiplexing
Here the Techopedia explains Multiplexer (MUX)
A TDM means Time division multiplexer choose samples of many signals having separate analog signals in telecommunications and attach them into wide-band analog signal of one pulse amplitude modulation (PAM).
In telecommunications, for digital signals on a computer network or with digital video, several variable bit-rate data streams of input signals (using packet mode communication) may be combined into one constant bandwidth signal. A limited number of constant bit-rate data streams of input signals may be multiplexed into one higher bit-rate data stream with an alternate method using a TDM. A multiplexer needs a DMUX (demultiplexer) to finish the process which means to separate multiplex signals carried by the single shared medium or device.
Sometimes, a multiplexer and a demultiplexer are combined into a single device permits the device to process both incoming and outgoing signals. A single output of multiplexer connected to a demultiplexer's single input over a single channel.
Applications of Multiplexers
A Multiplexer is used in numerous applications like, where multiple data can be transmitted using a single line.
Communication System –A Multiplexer is used in communication systems, which has a transmission system and also a communication network. A Multiplexer is used to increase the efficiency of the communication system by allowing the transmission of data such as audio & video data from different channels via cables and single lines.
Computer Memory –A Multiplexer is used in computer memory to keep up a vast amount of memory in the computers, and also to decrease the number of copper lines necessary to connect the memory to other parts of the computer.
Telephone Network –A multiplexer is used in telephone networks to integrate the multiple audio signals on a single line of transmission.
Transmission from the Computer System of a Satellite:
A Multiplexer is used to transmit the data signals from the computer system of a satellite to the ground system by using a GSM communication.
These are the different types of multiplexing techniques used in communication system for efficient transferring and receiving of the data. Hope you have got a better idea of all these types of multiplexing, and therefore, you can share your views on this article in the comment section below. And, also mention any of the practical examples of these multiplexing types – if you are interested.
Please refer to this link to know more about Difference b/w GSM and CDMA.
Design One Bit Full Adder Using Multiplexers
Source: https://www.watelectronics.com/what-is-multiplexer-and-types/
0 Response to "Design One Bit Full Adder Using Multiplexers"
إرسال تعليق